What are miniature bearings? (Informational Handbook)
Content
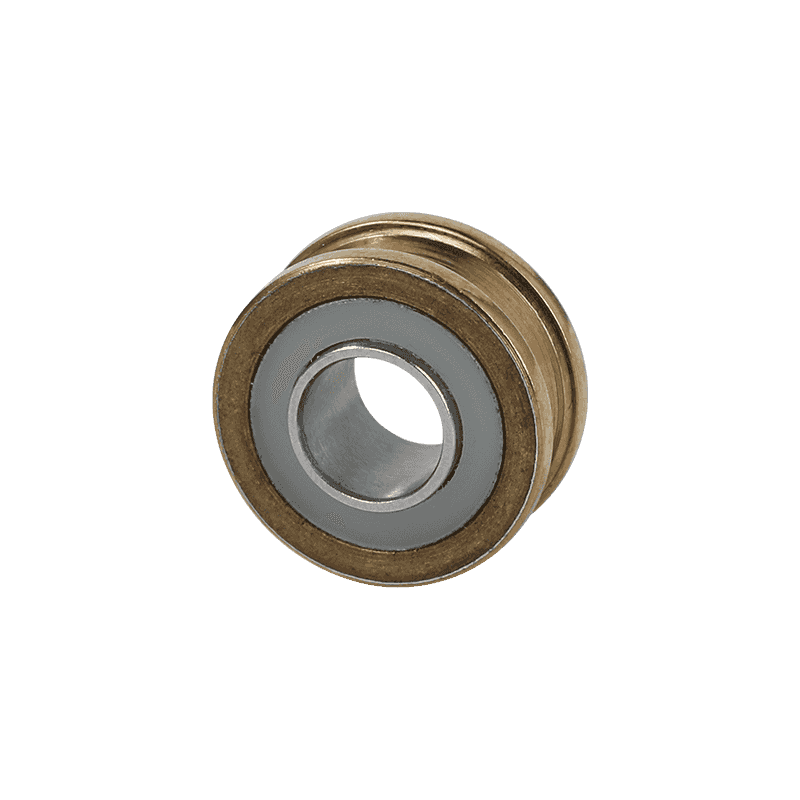
Miniature bearings are bearings that are exceptionally small in size, specifically designed for equipment where space is extremely limited but smooth and precise operation is required. You can think of them as miniature "rotating joints."
▸Core Definition: Super Small Rotating Helpers
--The core function of a bearing is to allow one component to rotate smoothly around another, while reducing friction and bearing load.
--Miniature bearings compress this function into a very tiny size. They are typically small, with outer diameters commonly ranging from a few millimeters to a dozen millimeters, and even smaller ones exist.
Although small, they are "small but perfectly formed," containing all the necessary key components.
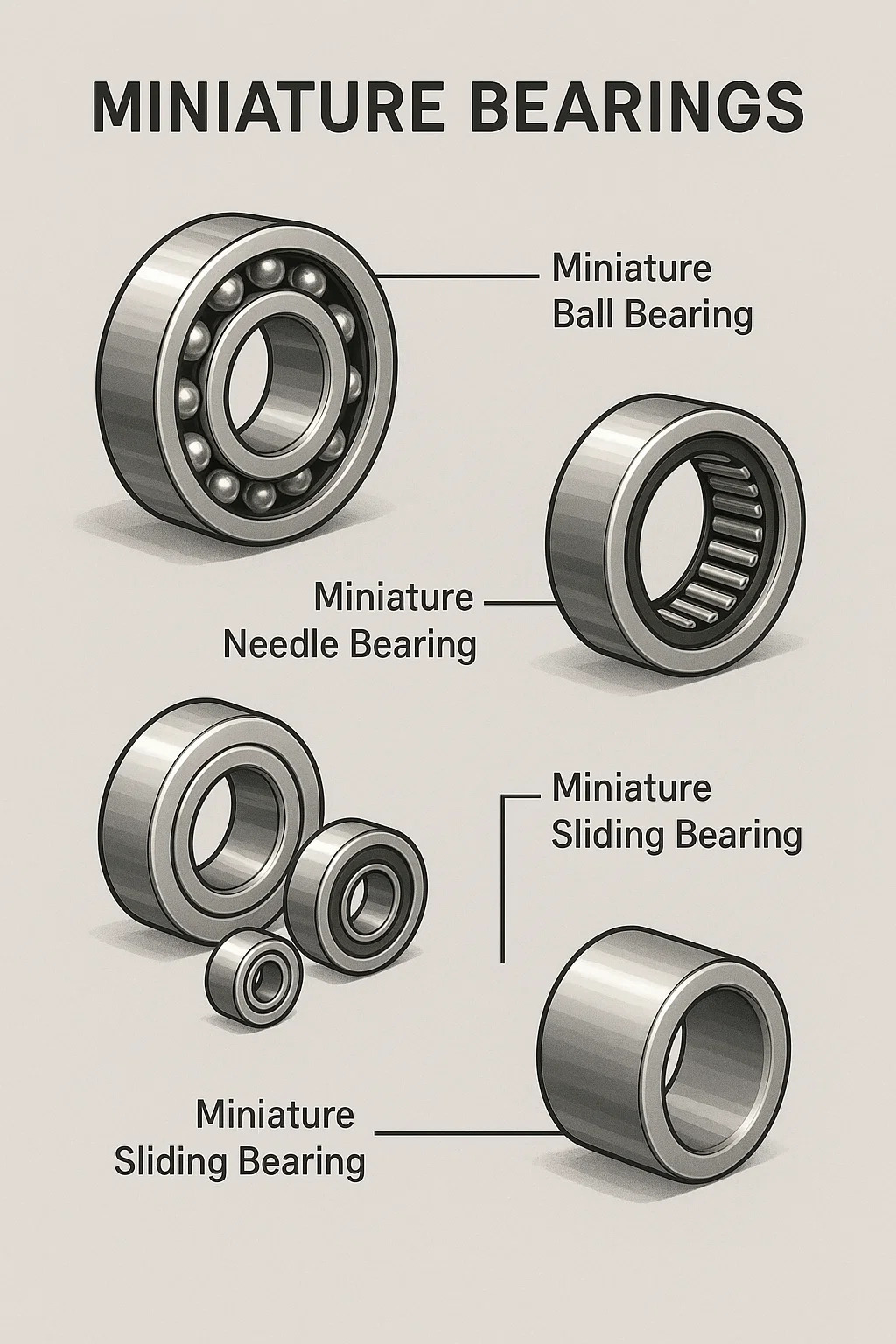
▸Main Types: More than just ball bearings
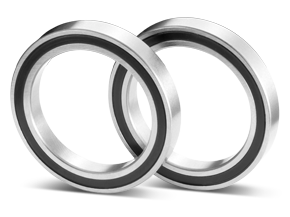
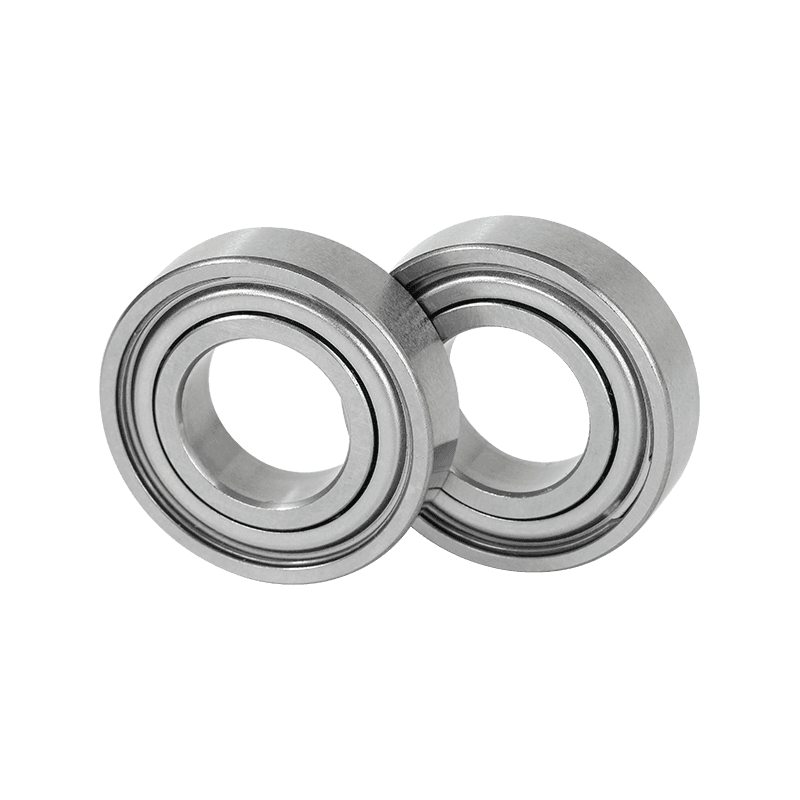
--Miniature Ball Bearings: This is the most common type of miniature bearing. It works by using tiny, hard balls (usually steel or ceramic) rolling in the tracks (raceways) of the inner and outer rings. We discussed how they work in detail earlier.
--Miniature Needle Bearings: This type of bearing uses slender "needles" (cylinders) instead of balls. It occupies a flatter and thinner space, making it particularly suitable for installation in areas with very narrow radial space but requiring the ability to withstand large radial forces (such as inside certain gears).
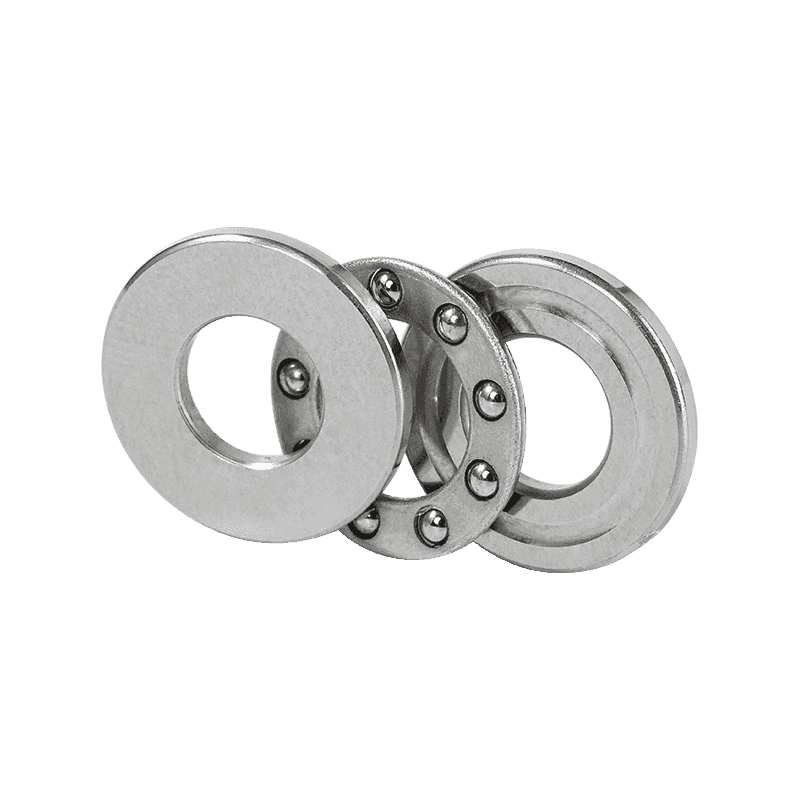
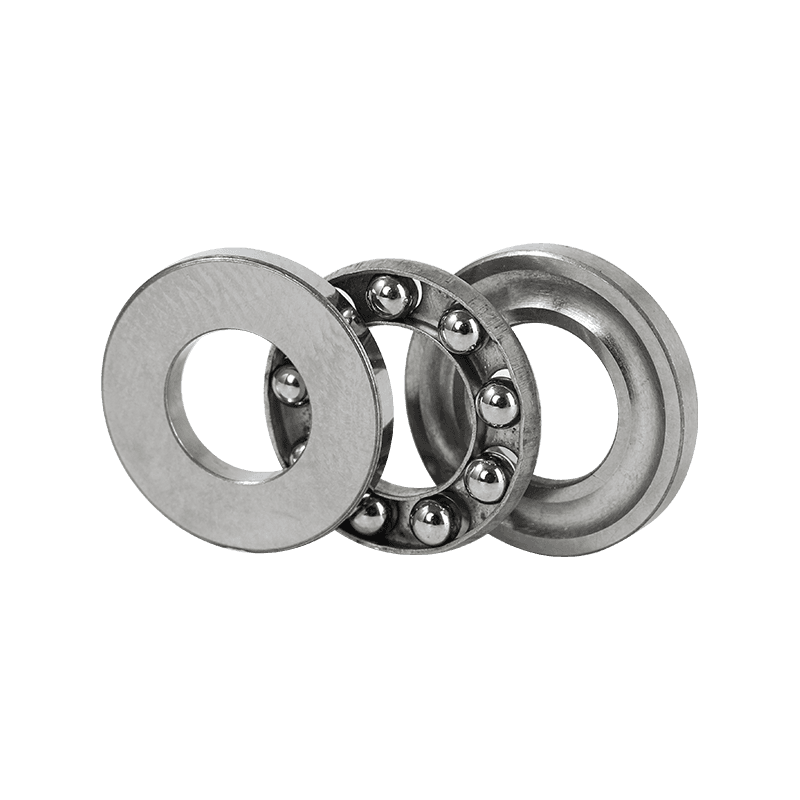
--Other Types: Depending on specific needs, there are also miniature sliding bearings (which rely on the sliding of smooth material surfaces), miniature angular contact bearings (which can withstand axial thrust), etc., but ball and needle bearings are the most common types of miniature bearings.
▸Key Features: Special Requirements Due to "Small Size"
--Ultra-High Precision: This is the biggest characteristic of miniature bearings! Because the size is so small, any manufacturing error—such as non-circular raceways, inconsistent ball sizes, or assembly deviations—will be magnified, leading to rough rotation, excessive noise, or even jamming. Therefore, the requirements for manufacturing precision are extremely strict.
--Special Materials: To achieve high precision, high strength, wear resistance, rust prevention, and even high-temperature resistance, miniature bearings usually use high-quality alloy steel, stainless steel (commonly used for rust prevention), or high-performance ceramics (for more special applications).
--Precision Lubrication: The space inside is so small that only a small amount of special grease (thick oil paste) or oil can be added. This lubricant must be very stable, long-lasting, and high-performing; a small amount can go a long way, ensuring smooth and quiet operation for extended periods.
--Sensitive to dirt and contamination: The internal space is small, and even a tiny amount of dust, fibers, or even moisture can get stuck in the raceway, causing the balls or needles to jam, leading to bearing damage. Therefore, many miniature bearings come with seals or dust covers to prevent contaminants from entering.
▸Where are they used? Small size, big impact
--Wherever precise, smooth, and reliable rotation is needed in extremely small spaces, miniature bearings are almost always present:
--Precision instruments and meters: Focusing knobs of microscopes, precision shafts of measuring equipment, rotating mechanisms in optical lenses.
--The heart of small motors: Drone motors, computer cooling fan motors, electric toy motors, electric toothbrush motors, small power tools (such as precision drills).
--Computers and office equipment: Hard drive motor spindles, optical drive laser head movement mechanisms, printer paper feed roller shafts.
--Medical devices: Dental handpieces (drills), small surgical instruments, internal components of precision testing equipment.
--Models and toys: Wheel axles of remote-controlled cars/boats/airplanes, transmission gearboxes, internal steering servos.
--Consumer electronics: Lens zoom motors and precision rotating shafts of high-end cameras.
--Automation equipment: Small robot joints, rotating components inside sensors.
▸Why are they so important? Precision equipment cannot do without them
--With miniature bearings, engineers can design increasingly smaller and more precise equipment.
--They ensure that the core rotating parts of these devices can:
--Rotate smoothly: Low resistance, high efficiency.
--Rotate accurately: Reduced wobble, ensuring accurate equipment operation.
--Rotate quietly: Good design and lubrication reduce noise.
--Rotate durably: Withstand certain forces and have a long service life in a clean environment.

 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch